Quaoar
The
Quaoar is a body that lies beyond the orbit of Pluto. Quaoar is one of the
Kuiper belt object. Quaoar is massive enough to be considered as a dwarf
planet, but it has not been classified as such yet. The Quaoar is discovered in
2020 by the American scientists Mike Brown and Chadwick Trujillo of the
California institute of Technology at the Palomar Observatory in California.
The Quaoar name is given after a creation god of the Native American Tongva Tribe.
In 2007, the American astronomer Brown found the tiny moon around the Quaoar,
Weywot. The name is given after the sky god, the son of Quaoar.
 |
| The Quaoar |
The
scientists believed that the Quaoar may be red in colour and coated with water
ice. In the distant past of Quaoar, it had an atmosphere with nitrogen, methane
and carbon monoxide. Because of low gravity of Quaoar, some of these molecules
bled away into space but methane stayed. The solar radiation gradually formed
hydrogen chins out of the carbon and hydrogen atoms. These hydrogen and carbon
atoms make up methane. This process is the cause for the red colour of Quaoar.
The
average distance between the Quaoar and the Sun is approximately 43.7 AU. The
closest distance from the Sun is 41.9 AU and farthest distance is 45.49 AU.
That means the Quaoar orbits the Sun in nearly circular orbit. The Quaoar
requires 288.83 Earth years to complete one trip around the Sun. The one day on
the Quaoar is nearly 9 hours long. But derived from the rotational light
curves, its rotation period is measured to be 17.68 hours. As the Quaoar is far
away from the Sun at an average distance of 43.7 AU, the Sun light requires 5
hours to reach the Quaoar.
Orcus – Anti Pluto
The
Orcus is one of the largest known Kuiper belt object. The Orcus is named after
the Roman god of the dead who severely punished those who broke their oaths. On
February 17th, 2004, Orcus was discovered by Michael Brown of
Caltech, David Rabinowitz of Yale University and Chad Trujillo of the Gemini
Observatory. The orbital properties of Orcus are much similar to the Pluto’s.
The Orcus has a moon orbiting around named as Vanth. The moon Vanth was
discovered by Michael Brown and T.A. Suer on 13 November 2005. The discovery
was announced on 22 February 2007. Like Charon compared to Pluto, Vanth is
quite large compared to Orcus and is one reason for characterizing Orcus as the
“Anti-Pluto”. If Orcus announced as dwarf planet, the Vanth would be the third
largest known dwarf planet moon after Charon and Dysnomia.
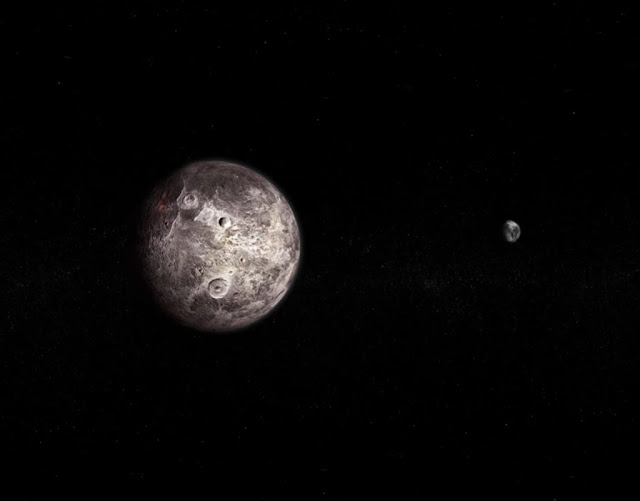 |
| The Orcus |
The
Orcus is locked in a 2:3 resonances with ice giant Neptune. This means, when
the Orcus making two revolutions around the Sun to every three of Neptune’s. This
resonance is much like Pluto. But except the phase of Pluto. The phase of orbit
of Orcus is opposite from Pluto. This means, when Orcus is at aphelion, the
Pluto is at perihelion and vice versa. The inclinations and eccentricities are
similar to the Pluto. Because of these contrasts and similarities, along with
the moons of both Orcus and Pluto. Because of these reasons the Orcus is called
as the “Anti-Pluto”.
The
closest distance between the Orcus and the Sun is 30.3 AU and the farthest
distance is 48.1 AU. The Orcus requires 245.19 Earth years to complete one trip
around the Sun with orbital inclination of 20.6 O to the ecliptic.
The astronomer Jose Luis Ortiz and colleagues assuming that the moon Vanth is
not tidally locked with the Orcus and according to this assumption they have
derived a possible rotation period of about 10.5 hours. So, the day on the
Orcus is 10.5 hours long.
Sedna
 |
| The Sedna: farthest known object. |
On
2020, the scientists found a large planetoid in the outer reaches of the solar
system. This planetoid is named as Sedna. The planetoid was named after the
Inuit goddess of the sea. The average distance of the Sedna from the Sun is
about 85 AU. The Sedna is about three times farthest than the Neptune. As the
Sedna is farthest known Trans-Neptunian Object, the Sun light requires 5 Earth
days to reach on its surface. The Sedna was discovered by the scientists
Michael Brown (Calteach), Chad Trujillo (Gemini Observatory) and David
Rabinowitz (Yale University). The astronomer Michael Brown initially given a
nickname to Sedna as “The Flying Dutchman” or “Dutch”, after a legendary ghost
ship, because the Sedna’s slow movement had initially masked its presence from
his team.
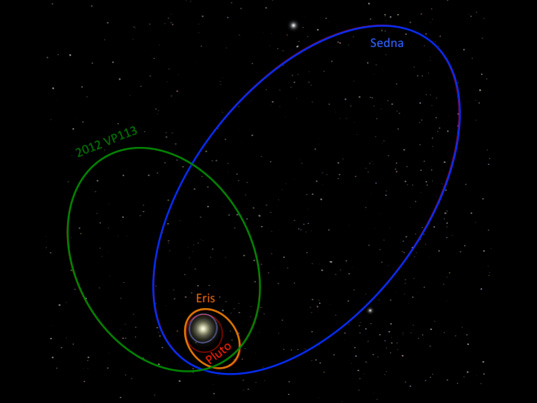 |
| Orbit of Sedna |
The Sedna has
the longest orbital period of any known object in the solar system. The orbital
period of Sedna is 11,400 Earth years. This orbital period is comparably very longest
among all known bodies of the solar system. The closest distance between the
Sedna and the Sun is 76.19 AU (perihelion) and the farthest distance 937 AU (Aphelion).
The average orbital speed of the Sedna is approximately 1 km per second. The rotational
period of Sedna is 10 hours. The discoverers of the Sedna not found any moon
around it. The Sedna’s closest approach to the Sun will come to perihelion
around July 2076. This is an opportunity to study the Sedna. This closest
approach of Sedna is very important because the next perihelion of Sedna will
be 12000 Earth years after.
Comments
Post a Comment